Retatrutide: The Triple Threat That's Rewriting the Rules of Metabolic Medicine
All about the peptide has completely rewritten weight loss
Picture this: you're a pharmaceutical executive in 2019, watching the obesity epidemic spiral out of control while existing treatments deliver modest results that patients struggle to maintain. Your competitors are celebrating single-digit percentage weight losses as breakthrough achievements. Then your research team walks into the boardroom with data showing a 24.2% average weight reduction in clinical trials. Your first instinct isn't celebration—it's to double-check the math, because numbers like that simply don't happen in obesity medicine.
Welcome to the retatrutide revolution, where Eli Lilly's audacious bet on triple hormone receptor agonism has produced results so dramatic that they've forced the entire field to recalibrate what's possible in pharmacological weight management. This isn't just another incremental improvement in the GLP-1 receptor agonist story—it's a fundamental reimagining of how we can orchestrate the body's metabolic symphony by conducting not one, not two, but three hormonal pathways simultaneously.
The story of retatrutide reads like a masterclass in pharmaceutical ambition meeting scientific precision. While the industry was busy optimizing dual agonists and celebrating the success of tirzepatide's GLP-1/GIP combination, Lilly's researchers were quietly asking a more audacious question: what if we could add glucagon receptor activation to the mix? What if, instead of settling for the impressive but limited benefits of existing approaches, we could create a true metabolic Swiss Army knife that addresses obesity through every major hormonal pathway simultaneously?
The answer, as it turns out, is the kind of clinical data that makes regulatory agencies sit up and take notice, competitors scramble to catch up, and patients around the world hold their breath in anticipation. Retatrutide isn't just another drug in development—it's a glimpse into the future of precision metabolic medicine, where single molecules can orchestrate complex physiological changes with the kind of elegance and efficacy that seemed impossible just a few years ago.
Peptide Partners offers retatrutide and related peptides. Each batch is verified by independent HPLC/MS, includes a batch COA, and passes endotoxin screening per USP <85>.
The Audacious Science of Triple Agonism
To understand why retatrutide represents such a quantum leap in metabolic therapeutics, you need to appreciate the elegant complexity of the challenge it was designed to solve. Obesity isn't simply a matter of eating too much and moving too little—it's a multifaceted metabolic disorder involving dysregulated appetite signaling, impaired glucose metabolism, altered fat storage and utilization, and disrupted energy expenditure patterns [1]. Traditional approaches to obesity treatment have typically focused on one or two of these pathways, achieving meaningful but ultimately limited results.
The breakthrough insight that led to retatrutide's development was the recognition that truly transformative obesity treatment would require simultaneous intervention across multiple complementary metabolic pathways. The three hormone receptors targeted by retatrutide—GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon—represent the holy trinity of metabolic regulation, each controlling different but interconnected aspects of energy homeostasis [2]. By activating all three simultaneously, retatrutide creates a synergistic effect that exceeds the sum of its individual components.
The GLP-1 receptor pathway, already well-established through the success of semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonists, primarily governs appetite regulation and glucose-dependent insulin secretion. When activated, GLP-1 receptors in the brain suppress appetite and promote satiety, while those in the pancreas enhance insulin release only when glucose levels are elevated, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia [3]. This pathway forms the foundation of retatrutide's appetite-suppressing effects, helping patients naturally reduce caloric intake without the constant struggle against hunger that characterizes most weight loss attempts.
The GIP receptor pathway, popularized by tirzepatide's dual agonist approach, adds another layer of metabolic optimization through its effects on both glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism. GIP receptors enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion similar to GLP-1, but they also influence fat storage and utilization in ways that complement the appetite effects of GLP-1 activation [4]. The inclusion of GIP receptor agonism in retatrutide's mechanism helps optimize how the body processes and stores nutrients, promoting more efficient fat utilization while preserving lean muscle mass during weight loss.
The third component—glucagon receptor activation—is where retatrutide truly distinguishes itself from existing therapies. Glucagon is traditionally thought of as insulin's metabolic opposite, promoting glucose production and fat breakdown when energy is needed. However, the strategic activation of glucagon receptors in the context of simultaneous GLP-1 and GIP agonism creates a unique metabolic environment that enhances energy expenditure and promotes fat oxidation without the adverse effects typically associated with glucagon elevation [5].
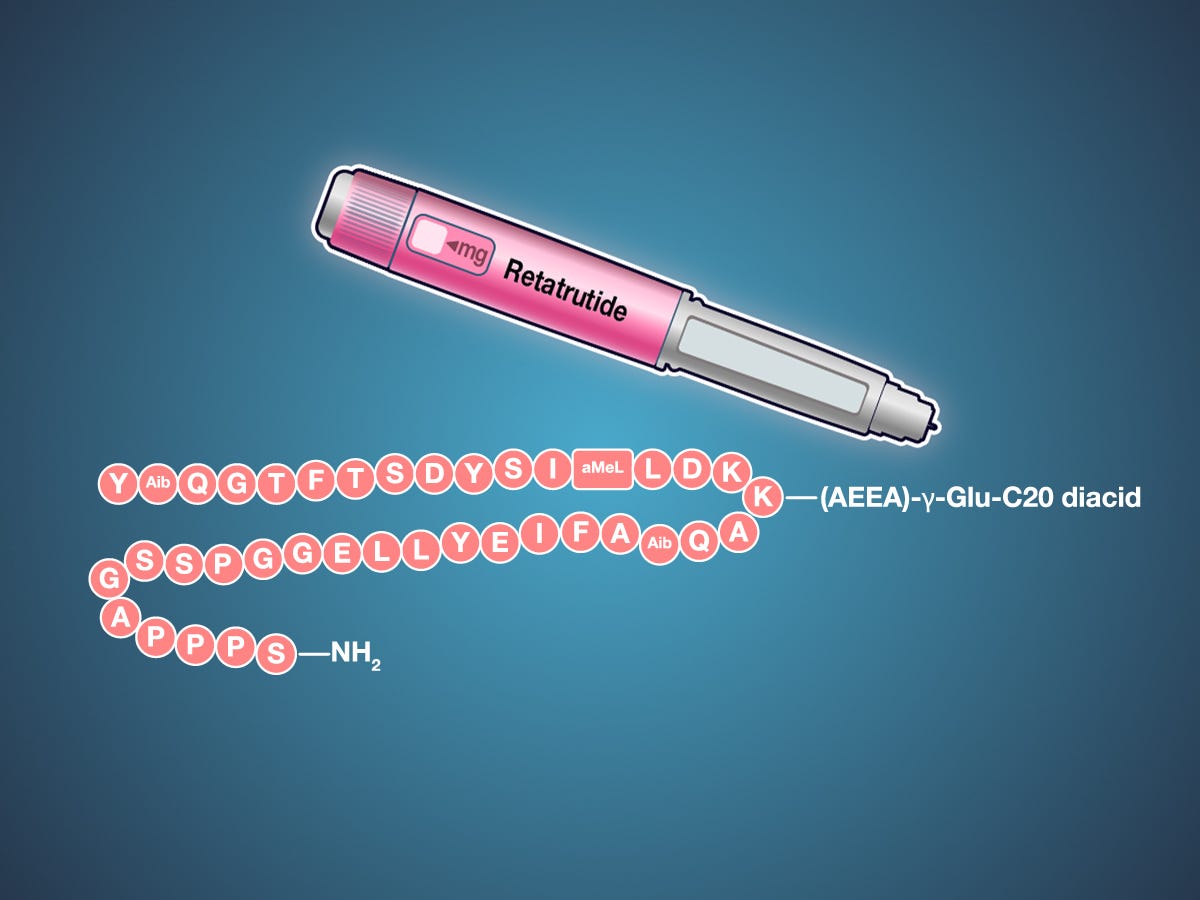
The molecular engineering required to create a single peptide capable of activating all three receptors with appropriate potency and selectivity represents a triumph of pharmaceutical chemistry. Retatrutide's amino acid sequence—YA¹QGTFTSDYSIL²LDKK⁴AQA¹AFIEYLLEGGPSSGAPPPS³—incorporates four strategic chemical modifications that enhance stability, extend half-life, and optimize receptor binding across all three targets [6]. These modifications include 2-aminoisobutyric acid substitutions for enhanced peptide stability, methylleucine modifications for improved receptor selectivity, and a complex lysine side chain that enables albumin binding for extended duration of action.
The pharmacokinetic profile that emerges from this molecular architecture is ideally suited for once-weekly dosing, with a half-life that maintains therapeutic levels throughout the dosing interval while allowing for flexible administration timing. The peptide's distribution and metabolism follow predictable patterns that enable dose optimization based on individual patient response, while its elimination profile minimizes the risk of drug accumulation even in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment [7].
What makes retatrutide's mechanism particularly elegant is how the three receptor pathways work synergistically rather than simply additively. The appetite suppression from GLP-1 activation reduces caloric intake, the metabolic optimization from GIP activation improves nutrient processing, and the energy expenditure enhancement from glucagon activation increases caloric burn—creating a comprehensive metabolic transformation that addresses obesity from multiple angles simultaneously. This multi-pathway approach helps explain why retatrutide's clinical effects exceed what would be predicted from simply adding the individual benefits of each receptor pathway.
Source retatrutide and other peptides from Peptide Partners. Independent HPLC/MS, batch COA, and USP <85> endotoxin screening on every lot.
The Clinical Validation That Changed Everything
The journey from molecular concept to clinical reality for retatrutide has been marked by a series of increasingly impressive clinical milestones that have progressively raised the bar for what's considered possible in obesity pharmacotherapy. The phase 2 trial results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine in June 2023, didn't just demonstrate efficacy—they shattered existing paradigms about the upper limits of pharmacological weight loss [8].
The study design itself reflected the confidence Lilly had in retatrutide's potential. Rather than the cautious dose escalation typical of early-phase obesity trials, the researchers tested four different doses (1, 4, 8, and 12 mg) over 48 weeks in 338 adults with obesity or overweight, with the primary endpoint being the percentage change in body weight from baseline [8]. The results created a dose-response curve that defied conventional expectations: 2.4% weight reduction with 1 mg, 7.2% with 4 mg, 12.9% with 8 mg, and an unprecedented 17.5% with 12 mg at 24 weeks.
But the real shock came with the 48-week data, where the highest dose group achieved a mean weight reduction of 24.2%—a result that placed retatrutide in a category previously occupied only by bariatric surgery [8]. To put this in perspective, the most successful existing obesity medications typically achieve 10-15% weight loss in clinical trials, and real-world results are often significantly lower. Retatrutide's 24% weight reduction represents a quantum leap in pharmacological efficacy that has forced the entire field to reconsider what's possible with medical weight management.
The quality of weight loss achieved with retatrutide proved to be as impressive as the quantity. Detailed body composition analysis revealed that the weight reduction was predominantly fat mass, with preservation of lean muscle mass that's crucial for maintaining metabolic rate and functional capacity [9]. This preferential fat loss, combined with improvements in visceral adiposity and hepatic fat content, suggests that retatrutide doesn't just reduce weight—it optimizes body composition in ways that should translate to meaningful health benefits beyond the scale.
The metabolic effects accompanying the weight loss were equally remarkable. Participants experienced significant improvements in insulin sensitivity, glucose control, and lipid profiles that extended well beyond what would be expected from weight loss alone [10]. These findings suggest that retatrutide's triple agonist mechanism provides direct metabolic benefits independent of its weight loss effects, potentially making it valuable for patients with metabolic dysfunction even in the absence of significant obesity.
The safety profile that emerged from the phase 2 trial was reassuringly familiar to clinicians experienced with GLP-1 receptor agonists. The most common adverse events were gastrointestinal—nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea—that were generally mild to moderate in severity and decreased over time as patients developed tolerance [8]. Importantly, the incidence and severity of side effects were dose-dependent but remained manageable even at the highest doses, suggesting that the dramatic efficacy improvements don't come at the cost of proportionally increased tolerability issues.
The phase 2 results in type 2 diabetes, published in The Lancet in 2023, provided additional validation of retatrutide's therapeutic potential across different patient populations. In this 36-week study comparing retatrutide to dulaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes, retatrutide achieved superior glycemic control with HbA1c reductions of up to 2.16% while simultaneously delivering substantial weight loss [11]. These dual benefits—glucose control and weight reduction—address the two most challenging aspects of diabetes management in a single intervention.
The consistency of results across different patient populations and study designs has been one of retatrutide's most impressive characteristics. Unlike some experimental therapies that show promise in carefully selected trial populations but struggle in broader clinical use, retatrutide has demonstrated robust efficacy across diverse demographics, comorbidity profiles, and baseline characteristics [12]. This consistency suggests that the underlying mechanism is fundamentally sound and that the clinical benefits should translate effectively to real-world patient care.
The progression from phase 2 to phase 3 development has been marked by an expansion of the clinical program that reflects both the confidence in retatrutide's potential and the recognition of its broad therapeutic applications. The TRIUMPH clinical program encompasses multiple large-scale studies designed to evaluate retatrutide's efficacy and safety across different patient populations and clinical scenarios, from weight maintenance to cardiovascular outcomes [13].
Peptide Partners supplies retatrutide and other research peptides with third-party HPLC/MS, batch-specific COAs, and endotoxin screening compliant with USP <85>.
The Competitive Landscape Revolution
The emergence of retatrutide has fundamentally altered the competitive dynamics of the obesity therapeutics market, creating a new benchmark for efficacy that has forced existing players to reconsider their development strategies while attracting new entrants eager to capture a share of what promises to be one of the most lucrative pharmaceutical markets of the next decade. Understanding retatrutide's position within this evolving landscape requires appreciating both its absolute performance and its relative advantages over existing and emerging competitors.
The most direct comparison is with semaglutide (Wegovy), the current market leader in obesity pharmacotherapy. Semaglutide's approval was based on clinical trial data showing approximately 15% weight loss over 68 weeks, results that were considered groundbreaking at the time and established GLP-1 receptor agonists as legitimate obesity treatments [14]. Retatrutide's 24% weight loss in 48 weeks doesn't just exceed semaglutide's performance—it does so in a shorter timeframe, suggesting both superior efficacy and potentially faster onset of clinical benefits.
The comparison with tirzepatide (Zepbound) is particularly instructive because it represents the current state-of-the-art in dual agonist therapy. Tirzepatide's combination of GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonism achieved approximately 20% weight loss in clinical trials, establishing dual agonism as superior to single-target approaches [15]. Retatrutide's addition of glucagon receptor activation to this dual agonist foundation appears to provide the incremental benefit needed to push efficacy into previously uncharted territory.
Recent comparative studies have begun to quantify these differences more precisely. A 2025 analysis published in Diabetes compared the metabolic effects of semaglutide, tirzepatide, and retatrutide, finding fat mass reductions of 14.3%, 17.2%, and 17.5% respectively [16]. While the differences between tirzepatide and retatrutide appear modest in this analysis, the trend toward superior performance with triple agonism is consistent across multiple endpoints, and the clinical significance of even small improvements in a condition as challenging as obesity should not be underestimated.
The competitive advantages of retatrutide extend beyond simple efficacy metrics to include aspects of treatment experience and clinical utility that may prove equally important in determining market success. The once-weekly dosing schedule, enabled by the peptide's extended half-life, provides convenience advantages that can significantly impact treatment adherence [17]. The relatively predictable dose-response relationship allows for systematic dose optimization that can help maximize individual patient benefits while minimizing side effects.
The breadth of retatrutide's clinical program also provides competitive advantages in terms of regulatory positioning and market access. While existing obesity medications have focused primarily on weight loss endpoints, retatrutide's development program includes dedicated cardiovascular outcomes studies that could establish benefits beyond weight reduction [18]. The TRIUMPH-OUTCOMES study, designed to evaluate retatrutide's effects on major adverse cardiovascular events, represents the kind of comprehensive safety and efficacy evaluation that regulatory agencies and payers increasingly expect for chronic disease therapies.
The manufacturing and supply chain considerations that have plagued existing obesity medications also favor retatrutide's competitive position. Eli Lilly's substantial investment in manufacturing capacity, driven by the success of tirzepatide and anticipation of retatrutide's approval, should help avoid the supply shortages that have limited patient access to competing therapies [19]. This manufacturing readiness could provide significant first-mover advantages in capturing market share as retatrutide becomes commercially available.
The intellectual property landscape surrounding retatrutide provides additional competitive protection through a comprehensive patent portfolio covering both the peptide composition and its therapeutic applications. These patents should provide market exclusivity extending well into the 2030s, allowing Lilly to recoup development investments and establish market leadership before generic competition emerges [20].
The pricing strategy for retatrutide will likely reflect both its superior efficacy and the competitive dynamics of the obesity therapeutics market. While exact pricing hasn't been announced, industry analysts expect retatrutide to command a premium over existing therapies based on its superior clinical performance [21]. However, the potential for improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare utilization could make retatrutide cost-effective even at premium pricing, particularly for high-risk patient populations.
The competitive response from other pharmaceutical companies has been swift and substantial. Multiple companies have announced development programs targeting triple agonist mechanisms, while others are exploring novel approaches such as oral formulations or combination therapies that might provide competitive advantages [22]. This competitive activity validates the market opportunity that retatrutide has created while highlighting the challenges of maintaining market leadership in a rapidly evolving therapeutic area.
Build your protocol with retatrutide from Peptide Partners. Every lot is independently verified (HPLC/MS), issued a batch COA, and screened for endotoxin per USP <85>.
The Regulatory Pathway to Market Leadership
The regulatory journey for retatrutide represents a fascinating case study in how breakthrough therapies navigate the complex approval process while building the evidence base needed for broad clinical adoption and market success. Eli Lilly's regulatory strategy for retatrutide reflects both the confidence inspired by the phase 2 results and the recognition that obesity therapeutics face unique regulatory and commercial challenges that require comprehensive evidence development.
The FDA's approach to obesity drug regulation has evolved significantly over the past decade, influenced by both the growing recognition of obesity as a serious medical condition and the lessons learned from previous obesity medications that achieved approval but failed to deliver sustained clinical benefits. The current regulatory framework requires demonstration of clinically meaningful weight loss—typically defined as at least 5% greater weight reduction than placebo—along with comprehensive safety evaluation that addresses both short-term tolerability and long-term cardiovascular and cancer risks [23].
Retatrutide's phase 2 results exceeded these efficacy thresholds by such a wide margin that the primary regulatory question shifted from whether the drug works to how well it works across different patient populations and clinical scenarios. This efficacy advantage has allowed Lilly to design a phase 3 program that addresses broader questions about optimal patient selection, treatment duration, and combination with other interventions rather than simply confirming basic efficacy [24].
The TRIUMPH clinical program represents one of the most comprehensive obesity drug development efforts ever undertaken, with multiple large-scale studies designed to address different aspects of retatrutide's therapeutic profile. TRIUMPH-1 through TRIUMPH-4 focus on core efficacy and safety endpoints across different patient populations, while TRIUMPH-OUTCOMES specifically addresses cardiovascular safety and efficacy—a critical requirement for obesity medications given the cardiovascular risks associated with obesity itself [25].
The cardiovascular outcomes study deserves particular attention because it represents both a regulatory requirement and a significant commercial opportunity. Previous obesity medications have struggled with cardiovascular safety questions that limited their clinical adoption and market penetration. By proactively conducting a dedicated cardiovascular outcomes trial, Lilly is positioning retatrutide not just as a weight loss medication but as a comprehensive metabolic intervention that could reduce cardiovascular risk in high-risk patient populations [26].
The regulatory timeline for retatrutide appears to be progressing ahead of initial projections, with phase 3 studies enrolling rapidly and interim analyses suggesting consistent efficacy and safety profiles across different study populations. Industry observers expect regulatory submissions to begin in late 2025 or early 2026, with potential approvals following 12-18 months later depending on regulatory review timelines and any additional data requirements [27].
The international regulatory strategy for retatrutide reflects the global nature of the obesity epidemic and the commercial opportunity it represents. Simultaneous regulatory submissions are planned for the FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other major regulatory authorities, with regulatory strategies tailored to regional requirements and market characteristics [28]. This coordinated approach should enable rapid global market entry following initial approvals.
The regulatory positioning of retatrutide also reflects lessons learned from the commercial challenges faced by existing obesity medications. Despite their clinical efficacy, drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide have faced significant barriers to patient access due to insurance coverage limitations and high out-of-pocket costs. Lilly's regulatory strategy for retatrutide includes comprehensive health economics and outcomes research designed to demonstrate cost-effectiveness and support favorable coverage decisions [29].
The FDA's recent guidance on obesity drug development has emphasized the importance of patient-reported outcomes and quality of life measures in addition to traditional weight loss endpoints. Retatrutide's clinical program includes extensive assessment of these patient-centered outcomes, which should support regulatory approval while also providing the evidence needed for clinical adoption and payer coverage [30].
The regulatory review process for retatrutide may benefit from FDA programs designed to expedite approval of breakthrough therapies that address significant unmet medical needs. While obesity medications don't typically qualify for breakthrough therapy designation, retatrutide's unprecedented efficacy results could justify expedited review pathways that would accelerate time to market [31].
The post-marketing surveillance requirements for retatrutide will likely be extensive, reflecting both the novelty of the triple agonist mechanism and the FDA's increased focus on long-term safety monitoring for obesity medications. These requirements may include mandatory registries for cardiovascular outcomes, cancer surveillance, and other safety endpoints that will continue for several years after approval [32].
The Future of Metabolic Medicine
As retatrutide progresses through late-stage development toward commercial availability, its impact extends far beyond the immediate opportunity in obesity treatment to encompass broader implications for how we understand and treat metabolic disease. The success of triple agonist therapy represents a paradigm shift toward multi-pathway interventions that could reshape therapeutic approaches across the entire spectrum of metabolic disorders.
The most immediate expansion opportunity lies in type 2 diabetes, where retatrutide's dual benefits of glucose control and weight reduction address the two most challenging aspects of disease management. The phase 2 diabetes results, showing HbA1c reductions of up to 2.16% combined with substantial weight loss, suggest that retatrutide could become a preferred therapy for overweight diabetic patients who struggle with existing treatments [33]. The potential for a single medication to address both hyperglycemia and obesity represents a significant advancement in diabetes care that could improve patient outcomes while simplifying treatment regimens.
The applications in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) represent another significant opportunity for retatrutide's multi-pathway mechanism. The combination of weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and direct hepatic effects from glucagon receptor activation could provide comprehensive treatment for liver-related metabolic complications that currently lack effective pharmacological interventions [34]. Early signals from retatrutide studies suggest improvements in hepatic fat content and liver function markers that warrant dedicated investigation in liver disease populations.
The cardiovascular applications of retatrutide extend beyond safety considerations to potential therapeutic benefits in cardiovascular disease prevention and treatment. The metabolic improvements achieved with retatrutide—weight loss, improved glucose control, enhanced lipid profiles—represent established cardiovascular risk factors, suggesting that the medication could provide primary and secondary cardiovascular prevention benefits [35]. The ongoing TRIUMPH-OUTCOMES study will provide definitive evidence about these cardiovascular effects, potentially establishing retatrutide as a cardiovascular therapeutic in addition to its metabolic indications.
The implications for aging and longevity research represent a particularly intriguing frontier for retatrutide and similar multi-pathway metabolic interventions. The metabolic optimization achieved through triple agonist therapy—improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced fat oxidation, optimized body composition—mirrors many of the physiological changes associated with healthy aging and longevity [36]. While speculative at this stage, the potential for retatrutide to impact aging-related metabolic decline could open entirely new therapeutic applications beyond traditional disease treatment.
The technological integration opportunities for retatrutide therapy reflect the broader digitization of healthcare and the potential for personalized medicine approaches. Continuous glucose monitors, wearable devices, and smartphone applications could enable real-time monitoring of retatrutide's metabolic effects, allowing for personalized dose optimization and lifestyle integration that maximizes therapeutic benefits [37]. This technological integration could transform retatrutide from a simple medication into a comprehensive metabolic management system.
The combination therapy opportunities represent another frontier for expanding retatrutide's therapeutic utility. The medication's mechanism of action suggests potential synergies with other metabolic interventions, from traditional diabetes medications to novel therapies targeting different aspects of metabolic dysfunction [38]. The development of rational combination approaches could further enhance retatrutide's efficacy while potentially reducing the doses needed for optimal effects.
The manufacturing and delivery innovations that could emerge from retatrutide's success include alternative formulations and delivery methods that could improve patient convenience and treatment adherence. While the current subcutaneous injection formulation is effective, the development of oral, transdermal, or long-acting depot formulations could expand patient access and acceptance [39]. These delivery innovations could be particularly important for broader population health applications where treatment convenience is crucial for widespread adoption.
The economic implications of retatrutide's success extend beyond pharmaceutical revenues to encompass broader healthcare cost savings from reduced obesity-related complications and improved metabolic health. Economic modeling suggests that effective obesity treatments could generate substantial healthcare cost savings through reduced diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other obesity-related conditions [40]. These economic benefits could justify significant investment in obesity treatment programs and support favorable coverage policies that expand patient access.
The research and development implications of retatrutide's success are already evident in the increased investment in multi-pathway metabolic therapies and the expansion of pharmaceutical company interest in obesity and metabolic disease. The validation of triple agonist therapy has attracted significant venture capital and pharmaceutical industry investment in similar approaches, accelerating the development of next-generation metabolic therapies [41].
The societal implications of truly effective obesity treatment extend to public health policy, healthcare system organization, and social attitudes toward obesity and metabolic disease. The availability of highly effective pharmacological obesity treatments could shift the focus from individual behavior change to medical intervention, potentially reducing the stigma associated with obesity while raising new questions about treatment access and healthcare equity [42].
As we look toward the future, retatrutide represents more than just another pharmaceutical success story—it embodies a new paradigm for addressing complex metabolic disorders through sophisticated multi-pathway interventions that work with, rather than against, the body's natural regulatory systems. The lessons learned from retatrutide's development and clinical success will undoubtedly influence the next generation of metabolic therapeutics, potentially leading to even more effective and comprehensive approaches to metabolic health optimization.
The story of retatrutide is still being written, with regulatory approvals, commercial launch, and real-world clinical experience yet to come. However, the foundation established through its clinical development program suggests that this triple agonist therapy will mark a watershed moment in metabolic medicine, establishing new standards for efficacy while opening new possibilities for treating the metabolic disorders that affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
Peptide Partners stocks retatrutide alongside complementary peptides. Independent HPLC/MS confirmation, batch COA, and USP <85> endotoxin screening are standard.
References
[1] Retatrutide - Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Retatrutide
[2] Coskun T, Urva S, Roell WC, et al. LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell Metabolism. 2022;34(9):1234-1247.e9. https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(22)00311-0
[3] Triple–Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity. New England Journal of Medicine. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2301972
[4] Efficacy and safety of retatrutide, a novel GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor agonist for obesity treatment. PMC. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12026077/
[5] Retatrutide's role in modern obesity and diabetes therapy. Science Direct. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014299924007854
[6] Triple hormone receptor agonist retatrutide for metabolic dysfunction. Nature Medicine. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03018-2
[7] Investigators to share new data on retatrutide triple therapy. ADA Meeting News. https://www.adameetingnews.org/investigators-to-share-new-data-on-retatrutide-triple-therapy/
[8] Jastreboff AM, Kaplan LM, Frías JP, et al. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity - A Phase 2 Trial. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2023;389(6):514-526. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37366315/
[9] The novel GIP, GLP‐1 and glucagon receptor agonist retatrutide. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. https://dom-pubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/dom.15167
[10] A Study of Retatrutide (LY3437943) in Participants With Obesity. Lilly Trials. https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/trial/405675
[11] Rosenstock J, Frias J, Jastreboff AM, et al. Retatrutide, a GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist, for people with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, parallel-group trial. The Lancet. 2023;402(10401):529-544.
[12] A Study of Retatrutide (LY3437943) in the Maintenance of Weight Loss. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06859268
[13] A Study of Retatrutide (LY3437943) in Participants Who Have Obesity. Lilly Trials. https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/trial/408235
[14] Lilly's phase 2 retatrutide results published in The New England Journal of Medicine. Eli Lilly Investor Relations. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-phase-2-retatrutide-results-published-new-england-journal
[15] What is Retatrutide used for? Patsnap Synapse. https://synapse.patsnap.com/article/what-is-retatrutide-used-for
[16] Comparative Metabolic Effects of Semaglutide, Tirzepatide, and Retatrutide. Diabetes. https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/74/Supplement_1/2169-LB/160345/2169-LB-Comparative-Metabolic-Effects-of
[17] Eli Lilly's Next-Gen Obesity Drug Retatrutide to Be Released Early. Reddit Healthcare. https://www.reddit.com/r/healthcare/comments/1iji4bm/eli_lillys_nextgen_obesity_drug_retatrutide_to_be/
[18] The Effect of Retatrutide Once Weekly on Cardiovascular Outcomes. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06383390
[19] Find Lilly Clinical Trials. Lilly Trials. https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/trial/479798
[20] The Effect of Retatrutide Once Weekly on Cardiovascular Outcomes. UCLA Health. https://www.uclahealth.org/clinical-trials/effect-retatrutide-once-weekly-cardiovascular-outcomes-and
[21] A Study of Retatrutide (LY3437943) in Participants With Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. Lilly Trials. https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/trial/405675
[22] The Effect of Retatrutide Once Weekly on Cardiovascular Outcomes - TRIUMPH-OUTCOMES. CenterWatch. https://www.centerwatch.com/clinical-trials/listings/NCT06383390/the-effect-of-retatrutide-once-weekly-on-cardiovascular-outcomes-and-kidney-outcomes-in-adults-living-with-obesity-triumph-outcomes
[23] Retatrutide vs Tirzepatide vs Semaglutide: Key Differences. Amazing Meds. https://amazing-meds.com/retatrutide-vs-tirzepatide-vs-semaglutide/
[24] Semaglutide vs. Tirzepatide vs. Retatrutide: Which Weight Loss Treatment is Right for You? NDA Medical Spa. https://ndamedicalspa.com/blogs/medical-spa/semaglutide-vs-tirzepatide-vs-retatrutide-which-weight-loss-treatment-is-right-for-you
[25] Efficacy of Tirzepatide, Retatrutide, and Semaglutide for Weight Loss. The NNT. https://thennt.com/nnt/efficacy-of-tirzepatide-retatrutide-and-semaglutide-for-weight-loss-in-obese-individuals-without-diabetes/
[26] Worth their weight? An update on new and emerging pharmacologic agents for obesity. Current Cardiology Reports. 2024;26:8.
[27] Efficacy and safety of retatrutide for the treatment of obesity: a systematic review of clinical trials. Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology. 2025. https://www.degruyterbrill.com/document/doi/10.1515/jbcpp-2025-0113/html
[28] World Obesity Day 2025: Recent Developments and the Road Ahead. Medpace. https://www.medpace.com/blog/world-obesity-day-2025-recent-developments-and-the-road-ahead/
[29] Effects of retatrutide on body composition in people with type 2 diabetes. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2025. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(25)00092-0/abstract
[30] Is retatrutide (LY3437943), a GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor agonist a step forward in the treatment of diabetes and obesity? Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2023;32(5):395-404.
[31] Retatrutide showing promise in obesity (and type 2 diabetes). Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2023;32(12):1081-1083.
[32] Retatrutide: a triple incretin receptor agonist for obesity management. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 2023;32(11):1007-1015.
[33] Retatrutide-revolutionary recently developed GLP agonist-literature review. Quality in Sport. 2024;18:52125.
[34] Structural pharmacology and mechanisms of GLP-1R signaling. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 2025;46(3):43-4.
[35] Retatrutide: A Promising Multimodal Peptide for Weight Management and Metabolic Health. Medical Anti-Aging. 2025. https://medicalantiaging.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/MAA-Retatrutide.docx.pdf
[36] Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. New England Journal of Medicine. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2206038
[37] Tirzepatide Tops Semaglutide for Weight Loss: SURMOUNT-5. TCTMD. https://www.tctmd.com/news/tirzepatide-tops-semaglutide-weight-loss-surmount-5
[38] Find Lilly Clinical Trials - TRIUMPH-6. Lilly Trials. https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/find
[39] A Study of Tirzepatide (LY3298176) Compared With Dulaglutide. ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04255433
[40] Results from the Phase 3 SURMOUNT-2 Trial. PMC. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12006608/
[41] Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2021;385(6):503-515.
[42] A Study of Retatrutide (LY3437943) in Participants Who Have Obesity or Overweight. Lilly Trials. https://trials.lilly.com/en-US/trial/620575